- What is Email Testing?
- Manual Email Testing
- Automated Email Testing
- Why You Can’t Ignore Email Testing
- Key Applications of Email Testing
- Ensuring Email Deliverability: Key Metrics to Monitor
- Reducing Email Bounce Rates
- Maximizing Email Open Rates
- Optimizing Email Delivery Times
- Minimizing Email Reject Rates
- Retrying Failed Delivery
- Validate Email Lists before Delivery (Email List Cleaner)
- Protecting Your Brand Reputation
- Lowering SPAM Score
- Virus Scanning
- Tracking List-Unsubscribe and Blocking
- Verifying Email Headers (SPF DKIM, DMARC, PTR, and BIMI)
- Ensuring Brand Logo is Displayed (VMC/BIMI)
- Enhancing User Experience
- Testing UI: Why email looks matter
- Checking Style & Font Consistency
- Verifying Client Support of Email Features
- Testing Correct Rendering in Different Devices
- Ensuring Content Accuracy & Spell Check
- Using Sandbox Campaigns: No More Ooops!
- Verifying Tracking Links for Analytics and User Engagement
- Ensuring Automated Email Responses and Triggers Execute as Planned
- Verifying Compliance with Regulations
- Handle User Unsubscribe Requests
- Manage Opt-in Email Lists
- Validating Applications and Servers are Running Correctly
- Essential role of Email in User Authentication and Login
- Disposable Inboxes for Testing
- Types of Email Testing
- Content Testing
- Template Rendering
- Image and Style Accuracy
- Overall Content Accuracy
- Functional Testing
- Email Sending/Receiving Functionality
- Verifying Email Filters and Rules
- Compatibility Testing
- Cross-Platform and Cross-Device Testing
- Email Client Compatibility
- Performance Testing
- Load Testing for Email Servers
- Email Delivery Speed Testing
- Disposable Mailbox Testing
- What Are Disposable Email Accounts?
- Benefits of Using Disposable Emails
- How to Set Up Disposable Email Accounts
- Integrating Disposable Emails with Testing
- Email Testing Challenges
- Handling Various Email Clients
- Maintaining a Collection of Devices and Accounts
- Managing Multiple Logins
- Time-Consuming Process
- Ensuring Responsive Design
- Testing Across Different Email Service Providers
- Dealing with Spam Filters
- Monitoring Email Reputation
- Real-World Email Testing Scenarios
- E-commerce Transactional Emails
- Newsletter Campaign Testing
- Registration and Verification Emails
- Security: Password Reset and Account Recovery
- How to Test Emails Like a Pro
- Manual Testing
- Content, Spam and Virus Checks
- Test Campaign Effectiveness
- QA Testing for Apps and Software
- Testing Mailserver Rules and Routing
- SMTP Server Inspections
- Automating Your Email Testing
- Benefits of Automation
- Popular Testing Tools and Frameworks
- Test Automation Best Practices
- How You Can Apply Automation to Email Processes
- Testing Developer Environments - production and staging environments
- Background Email Scanning and Event Notifications
- Conclusion
Master the art of email testing with our definitive guide, exploring effective strategies and best practices to enhance delivery, deliverability, engagement, and conversion rates.
Ensuring an email reaches its intended recipient involves much more than a simple click of the 'send' button. There are numerous challenges to consider: your emails could bounce back, be outright rejected, or end up flagged as spam. Even if an email successfully lands in the intended inbox, it might face issues like incorrect rendering or contain errors in text, images, broken links, or personalization, not to mention the risk of being ignored due to the lack of an engaging subject line. This critical realization is at the heart of email testing, an essential practice for developers, QA testers and, increasingly, marketing teams deeply involved in software development, application maintenance and email campaigns.
Wondering how to properly test an email before hitting "send"? Don't worry, we're here to guide you. In this article, we delve into the multifaceted world of email testing, highlighting its crucial role, varied methods, and best practices. We'll cover content rendering, deliverability optimization, and how to enhance email reliability. Plus, we'll explore practical strategies and tools that streamline email testing, and empower you to achieve optimal delivery and engagement.
What is Email Testing?
Email testing is a systematic process of evaluating and verifying the functionality, accuracy, and reliability of email communications within software applications, websites, or email marketing campaigns. This testing involves various aspects, including sending, receiving, and processing emails, to ensure that they are delivered correctly, contain the expected content, and adhere to predefined criteria.
Email testing helps identify and address issues such as formatting errors, broken links, missing information, security vulnerabilities, and compliance with industry regulations. Ultimately, it guarantees that email communications are successfully delivered, error-free, secure, and provide a positive user experience. Both manual and automated testing methods are employed to achieve these objectives, each offering unique benefits in the testing process.
Manual Email Testing
This involves a hands-on approach where each element of an email is scrutinized by individuals. It includes checking email content for accuracy, ensuring links are functional, and verifying that layouts render correctly across various email clients and devices. Manual testing is crucial for personalizing content, catching nuanced errors, and understanding the user experience from a human perspective. The downside of manual email testing is that it's time-consuming and prone to human error. While it offers detailed inspection, it's inefficient for large-scale campaigns and can miss inconsistencies that automated systems would catch.
Automated Email Testing
Automated email testing employs software tools for a systematic and repetitive analysis of emails, crucial for any large-scale email campaign. In theory, you can automate any aspect of email testing that you'd typically do manually. Frequent uses include ensuring e mail deliverability and avoiding spam filters, validating content across various platforms, and efficiently handling large-scale performance analysis. For scenarios where manually reviewing each email is too time-costly or resource-demanding, automation proves indispensable.
Why You Can’t Ignore Email Testing
The significance of email testing is hard to overstate. For businesses relying on emails to connect with customers, application developers building authentication flows and marketing campaigns, or marketers focused on email display and delivery, email functionality is critical, which necessitates reliable and trustworthy testing.
Key Applications of Email Testing
Let's explore where email testing really makes an impact.
Ensuring Email Deliverability: Key Metrics to Monitor
While email delivery means getting your email to the recipient's server, email deliverability is about landing it in the inbox, not the spam folder. Email testing is often employed to increase email deliverability in following ways:
Reducing Email Bounce Rates
Bounce rates are a critical metric in email campaigns, reflecting the percentage of emails that weren't successfully delivered. High bounce rates can indicate issues with email addresses or server reputation, which can be rectified through proactive email testing and list cleaning.
Maximizing Email Open Rates
The open rate is a direct measure of engagement. Regular testing and optimization of subject lines, content, and sending times can significantly improve these rates, driving better campaign results.
Optimizing Email Delivery Times
Timing can be everything. Determining optimal delivery times through testing maximizes email visibility and engagement.
Minimizing Email Reject Rates
Monitoring and analyzing reject rates help in identifying and resolving issues that lead to emails being rejected by recipient servers, which is crucial for maintaining smooth communication channels.
Retrying Failed Delivery
Testing mechanisms to retry failed deliveries makes certain that temporary issues don't lead to permanent communication breakdowns.
Validate Email Lists before Delivery (Email List Cleaner)
Regular cleaning of email lists through testing helps in maintaining a database of valid, active email addresses, thereby improving overall campaign effectiveness.
Protecting Your Brand Reputation
Emails significantly influence brand reputation. Spam flags, unprofessional appearances, and failure to adhere to standards can harm a brand's image. Email testing is essential to avoid these issues and maintain brand integrity and trustworthiness. Here's how:
Lowering SPAM Score
Monitoring and optimizing for lower spam scores through testing ensures emails reach the inbox, not the spam folder, maintaining the integrity of the brand.
Virus Scanning
Testing emails for viruses and triggering elements helps make sure your emails are secure and trusted by recipient email servers and users.
Tracking List-Unsubscribe and Blocking
Monitoring unsubscribe rates and blocks through testing is vital for understanding recipient preferences and maintaining a positive brand image.
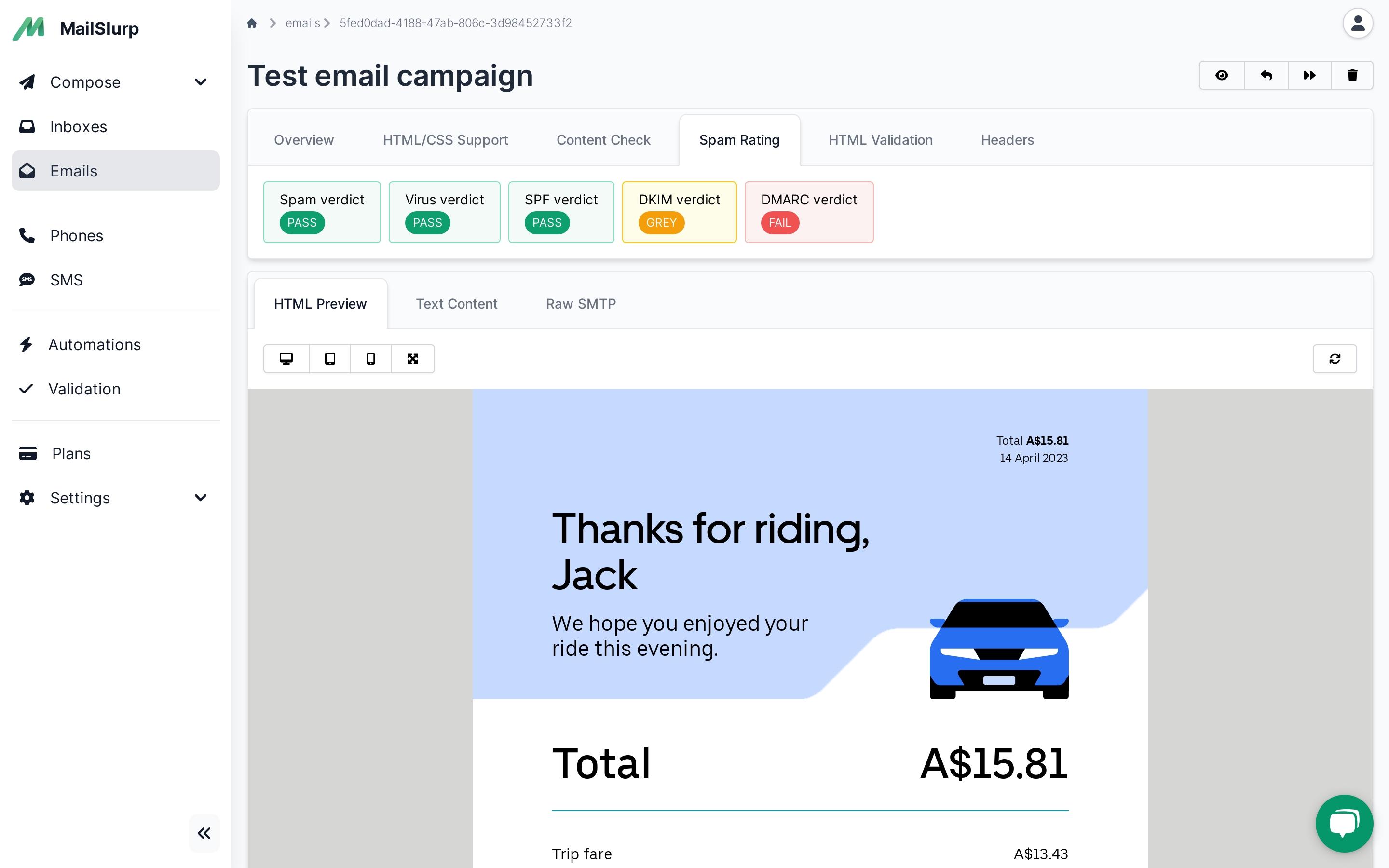
Verifying Email Headers (SPF DKIM, DMARC, PTR, and BIMI)
Testing and verifying email headers like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protects authentication and sender reputation, crucial for brand protection and email deliverability.
Ensuring Brand Logo is Displayed (VMC/BIMI)
Testing for Visible Mail Certification (VMC) and Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI) checks that brand logos are displayed in clients like Gmail, increasing brand presence.
Enhancing User Experience
Email testing is often employed to verify and improve the User Interface (UI) and User Experience of emails:
Testing UI: Why email looks matter
The visual appeal of an email significantly impacts user engagement. Testing for correctly rendered emails makes sure that your message is not just seen but also resonates with the recipient, enhancing the potential for engagement, conversions and customer loyalty.
Checking Style & Font Consistency
Testing for consistent formatting, styling, and font usage confirms that emails look professional and are easily readable across different platforms.
Verifying Client Support of Email Features
Testing across different email clients confirms compatibility and a uniform experience for all recipients.
Testing Correct Rendering in Different Devices
- Validating Responsive Email Across Clients: Using responsive email testing tools confirm emails are displayed correctly across various clients like Mail, Gmail, Outlook, etc.
- Handling Device Variability (iPhone, Tablet, Desktop, etc.): Responsive email testing across different devices addresses the challenge of emails being designed on desktops while most emails are read on mobile. This helps in preventing display issues that could affect user experience and conversion rates.
Ensuring Content Accuracy & Spell Check
Accurate and error-free content is fundamental in email communication. Testing for content accuracy and performing spell checks prevent misunderstandings and maintain the professionalism of your emails.
Using Sandbox Campaigns: No More Ooops!
Making use of sandbox environments for testing email campaigns allows you to catch and rectify errors before they reach your audience, preventing potentially embarrassing mistakes.
Verifying Tracking Links for Analytics and User Engagement
Testing tracking links makes certain they work correctly, providing valuable analytics and enhancing user engagement.
Ensuring Automated Email Responses and Triggers Execute as Planned
Testing automated responses and triggers guarantees that these function as intended, crucial for maintaining user engagement and operational efficiency.
Verifying Compliance with Regulations
Email testing can also be used to confirm email compliance with regulations, thereby helping you avoid legal penalties, maintain data privacy, and build trust with customers. Here’s how:
Handle User Unsubscribe Requests
Testing for efficient handling of unsubscribe requests is crucial for compliance and maintaining user trust.
Manage Opt-in Email Lists
Regular testing and management of opt-in email lists supports adherence to regulations and respect for user preferences.
Validating Applications and Servers are Running Correctly
Email can be used to test that servers, mobile, and web applications are working as expected. By generating test email accounts you can test login functionality and in-app messaging.
Essential role of Email in User Authentication and Login
It's imperative to use real emails in testing to confirm the effectiveness of user authentication and login procedures within applications. This verifies that these crucial functionalities operate as intended, providing a secure and reliable user experience.
Disposable Inboxes for Testing
Using disposable inboxes to test essential email-dependent functionality within apps and software guarantees robustness and reliability.
Types of Email Testing
Email testing encompasses a variety of types, each targeting specific aspects of email communication to ensure overall quality and effectiveness.
Content Testing
Content testing scrutinizes the accuracy and presentation of email content.
Template Rendering
Tests are conducted to guarantee templated names and variables display correctly in each email, preserving personalization. This is achieved through a combination of automated tools and manual checks that verify dynamic content rendering in different email scenarios.
Image and Style Accuracy
The focus here is on confirming that images and styles render as intended across various platforms, maintaining visual appeal and brand consistency. This involves testing emails on multiple devices and email clients.
Overall Content Accuracy
This crucial step guarantees the correctness of text, links, attachments, and overall formatting. It combines rigorous proofreading with functionality tests to deliver error-free and user-friendly content.
Functional Testing
This type assesses the operational functionality of email systems.
Email Sending/Receiving Functionality
Tests are conducted in various network conditions to verify reliable sending and receiving of messages, ensuring the system's robustness.
Verifying Email Filters and Rules
Simulations of different scenarios are able to confirm that email filters and rules are effective in sorting emails and preventing spam.
Compatibility Testing
This testing guarantees uniform performance across various environments.
Cross-Platform and Cross-Device Testing
Emails are tested for consistent display and functionality on different devices and operating systems, using responsive design testers and manual checks.
Email Client Compatibility
This guarantees emails appear correctly in various email clients, checking for any layout or functionality issues.
Performance Testing
This type evaluates the efficiency of email servers.
Load Testing for Email Servers
The server’s ability to handle large volumes of emails efficiently is tested by simulating high-volume email sending.
Email Delivery Speed Testing
Delivery times are measured to ensure swift email delivery, tweaking server configurations for optimal performance when necessary.
Disposable Mailbox Testing
The focus here is on utilizing temporary email addresses for safe testing.
What Are Disposable Email Accounts?
These are short-lived email addresses used for testing without impacting real user accounts.
Benefits of Using Disposable Emails
They offer a controlled environment for testing, preventing data leaks and spam to real users, ideal for testing various email functionalities.
How to Set Up Disposable Email Accounts
Setting up these accounts involves creating and managing them through specialized tools designed for disposable email testing.
Integrating Disposable Emails with Testing
These accounts are integrated into automated test suites, simulating real-world email interactions and enhancing the robustness of testing strategies.
Email Testing Challenges
Email testing, while essential, comes with its own set of challenges that can impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the process.
Handling Various Email Clients
One of the significant challenges in email testing is ensuring compatibility across a diverse range of email clients and devices.
Maintaining a Collection of Devices and Accounts
Keeping an up-to-date collection of all the different device types and email accounts for testing purposes can be daunting. This requires continuous updates as new devices and email client versions are released.
Managing Multiple Logins
Remembering login details for numerous email accounts like Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook, etc., adds to the complexity. This often necessitates a robust system for managing these credentials securely.
Time-Consuming Process
Testing in different email clients, making adjustments, and re-testing can be extremely time-consuming. Automating this process without tools like MailSlurp is challenging, as each client may render emails differently.
Ensuring Responsive Design
Responsive design is crucial for emails as it ensures that they render correctly on any device, be it a desktop, tablet, or smartphone. Achieving and testing this responsiveness across various devices and screen sizes is a complex task.
Testing Across Different Email Service Providers
Different email service providers (ESPs) have their own set of rules and algorithms for handling emails, which can affect deliverability and presentation. Testing across these various ESPs is essential to accomplish consistent email performance.
Dealing with Spam Filters
Navigating through spam filters is another critical aspect of email testing.
Monitoring Email Reputation
Determining what percentage of outbound emails are marked as spam or flagged as a virus by recipients is vital. Understanding and monitoring email reputation, as well as how many emails actually reach customers, requires advanced tools. Using MailSlurp's reputation and delivery monitoring graphs can provide valuable insights into these metrics. These challenges highlight the importance of employing sophisticated tools and strategies in email testing to overcome potential hurdles and guarantee that the emails not only reach their destination but also achieve their intended impact.
Real-World Email Testing Scenarios
Email testing plays a pivotal role across various scenarios. Here are some real-world applications:
E-commerce Transactional Emails
Consider an online store's checkout system you're developing. It's vital that the order confirmation and shipping notification emails trigger correctly upon purchase. Email testing ensures these transactional messages are reliably sent, avoiding customer service issues and maintaining the credibility of your e-commerce platform.
Newsletter Campaign Testing
Before launching a major newsletter campaign, it's imperative to conduct thorough testing. Consider the scenario of sending an email to thousands of subscribers only to discover it contains broken links or spelling errors. Such mistakes can not only diminish the impact of the campaign but also harm the brand's reputation. Pre-launch testing of newsletters helps identify and rectify such issues, protecting the campaign’s success.
Registration and Verification Emails
For software and applications, the registration and verification process often involves sending emails to users. These emails need to be clear, concise, and reliable. Email testing in this context is vital to making sure the user's journey from signing up to getting verified is smooth and free from technical glitches, avoiding unnecessary churn.
Security: Password Reset and Account Recovery
Emails related to password resets and account recovery are highly sensitive. Automated testing of these processes is crucial to security and user-experience. Testing helps verify that such emails are sent promptly and contain accurate, secure links, thereby safeguarding user accounts and maintaining the integrity of the system.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of email testing. Through these scenarios, you can see how crucial thorough email testing is in real-world contexts. It’s not just about making sure emails look good or land in the right inbox; it's about creating seamless, secure, and effective communication channels that serve your overall business’s operations and goals.
How to Test Emails Like a Pro
Manual Testing
Sometimes it is hard to automate a test, that is when manual testing is key.
Content, Spam and Virus Checks
- Email Preview: This involves viewing emails before they are sent to confirm layout, design, and content appear as intended across various email clients.
- Spam Testing: Testing emails against spam filters to make sure they don't get marked as spam.
- Virus Testing: Checking emails for potential threats that could be flagged by antivirus software.
- Email Validation: Ensuring HTML and CSS in emails are valid and compliant with web standards for consistent rendering.
Test Campaign Effectiveness
- Email Account Health Monitors: Monitoring the health of email accounts to maintain a good sender reputation.
- A/B Testing: Comparing different versions of emails to see which performs better in terms of open rates, click-throughs, and conversions.
- Email Deliverability Check: Assessing if emails are successfully reaching the recipient's inbox.
- Testing Links and Attachments: Confirming that all links and attachments in the email are functioning correctly.
- Verifying HTML/CSS Rendering: Validating emails render correctly across different email clients and devices.
QA Testing for Apps and Software
- Testing applications and software that require email addresses for sign-up and login to make sure email functionality integrates seamlessly.
Testing Mailserver Rules and Routing
- Using blank email addresses to test mail server rules and routing configurations.
SMTP Server Inspections
- Evaluating SMTP server settings and performance to secure reliable email delivery.
Automating Your Email Testing
Automated tests are test cases we describe in code or code-like files and let a computer run automatically. These can be used to test complex systems much faster than traditional manual testing.
Benefits of Automation
Efficiency and Continuity: Automation saves time and allows for continuous testing to identify and resolve issues swiftly.
Popular Testing Tools and Frameworks
- Browser-based tools like Selenium, Robot Framework, Cypress, Playwright.
- UI-based test tools such as Insomnia, Postman, and other open-source alternatives
Test Automation Best Practices
Implementing best practices in automation to achieve comprehensive and effective testing.
How You Can Apply Automation to Email Processes
- Transactional Email Testing: Using disposable mailboxes to test changes to APIs and transactional email functionalities.
- User Authentication Testing: Employing browser test tools to create disposable email accounts and test user authentication and email login processes.
Testing Developer Environments - production and staging environments
- Using disposable email accounts to login to staging environments.
- Iterating on product ideas and email campaigns based on test feedback.
Background Email Scanning and Event Notifications
- Automatically forwarding outbound emails to a service like MailSlurp for scanning and notifications on test failures, such as spam ratings.
By employing a mix of manual and automated testing methods, you can achieve the highest standards of email delivery and effectiveness.
Conclusion
We've covered a lot about email testing, emphasizing its importance in everything from e-commerce to app development. It's not just about avoiding the embarrassment of a typo; it's about ensuring your emails actually do what they're supposed to do - whether that's driving sales, getting users to click a link, or just confirming an account.
For the developers, QA testers, and marketers out there, it's clear that solid email testing practices can make or break your project's success. This isn't an area to cut corners. Regular, thorough testing can save you from a world of trouble, from lost customers to tarnished brand reputation.
This is where a tool like Mailslurp comes in. It's designed to tackle the challenges you face in email testing, providing features like detailed spam score analysis, rendering previews across different email clients, and the ability to use disposable email addresses for testing. MailSlurp isn't just another tool; it's a solution that addresses the specific needs you encounter in your day-to-day work.
Remember, good email testing can be the difference between a smooth launch and a frustrating day sorting out support tickets. So, take these insights, apply them, and watch as your email game gets stronger.